How Netflix Acquired 200M+ Paying Customers
The Growth Strategies Used to Become a Global Streaming Giant
Netflix (originally known as Kibble) was founded by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph in 1997. What started as a physical DVD rental business became one of the biggest tv and movie platforms, studios, and streaming businesses.
Strategy 1: Personalization at Scale
Netflix leverages machine learning and AI to provide a personalized experience of suggestions based on your preferences. Powerful search algorithms provide users with unique experiences to capture as much of their attention as possible.
Making their product not a one size fits all led to increasing engagement rates. The average number of daily minutes spent by US adults has grown 58% since 2017. Therefore as they learn more about their users, they provide better experiences that lead to higher engagement.
Strategy 2: Phased Expansion
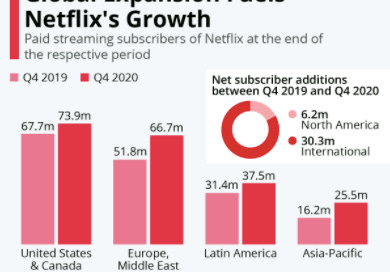
Starting in 2010, Netflix began a 3 part global expansion. They first expanded (from the US) into Canada because it was their most similar market, This stage was key as they learned how to adapt to different markets and how to execute expansion.
They expanded to 50 markets, based on attractiveness of the market, broadband internet and presence of affluent customers. The expansions helped Netflix learn more about users preferences, which helped improve the experience while ensuring it’s flexible to worldwide users.
Strategy 3: Focus on Pillars
Their product strategy was developed around 4 key pillars. This allowed them to always make progress and move the needle in the areas that mattered most
1. Personalization
2. Original content
3. Watching experience
4. Interactive storytelling
Strategy 4: DHM
Netflix’s product strategy is described as DHM by Gibson Biddle, former VP of product. It stands for Delight customers in Hard to copy, Margin-enhancing ways.
What started off as next day deliver to delight customers turned to it’s GLE strategy - streaming.
GLE stands for Get big, Lead, and Expand - their long term product vision. For Netflix, this became a 10-15 year growth path for the future.
This was initially leading in DVD distribution service, then leading the industry in streaming, and eventually expanding globally.
Netflix’s had a huge competitive advantage, their relationship with Hollywood, which was something that competitors could not easily copy.
As well, Netflix is available on almost every device through wifi, generating an audience and distribution that’s tough to replicate.
Strategy 5 : Paradox of Choice
Paradox of choice exists when there are too many options, often leading to stress or no decision. Many think more is better, but Netflix strives to reduce choice overload by customizing. They gives you less options, making it easier to pick.
Strategy 6: Cultivating Culture
Netflix started the culture of binge watching, making it a trend. Compared to live tv shows where you have to wait for a new episode every week, they choose to launch entire series in full to get people hooked.
This makes the experience exciting, thrilling, and addicting. Just like scrolling through social media, we crave what’s to see next. The human brain produces domaine when we binge watch, which Netflix learned and uses to their advantage
They learned how to get people hooked.
Netflix Today:
208M paying customers in Q1 2021
Responsible for 14.92% of global app traffic share
47% of American prefer Netflix over other streaming services
Keys to Growth Success:
Personalization at scale
Focus on core pillars
DHM + GLE
Phased Expansion
If you enjoyed this thread:
1. Subscribe to my SubStack for a more in depth breakdown of Native's growth
https://thegrowthplaybook.substack.com/welcome
2. Follow me on Twitter @growth_student for a new growth thread like this every week :)
https://twitter.com/growth_student
Sources:
https://productled.com/blog/netflixs-2020-product-strategy/
https://www.usertesting.com/blog/3-key-product-strategies-we-learned-at-ny-product-conference
https://www.statista.com/topics/842/netflix/
https://uxdesign.cc/netflix-vs-decision-fatigue-how-to-solve-the-paradox-of-choice-888ca56db4b
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/part-1-4-pillars-outcomes-driven-business-model-sundeep-sanghavi/